Philadelphia Chromosome Karyotype. The philadelphia chromosome is a specific genetic change that has become a sort of landmark in medicine, useful for identifying certain cancers by its presence and other cancers by its absence. …abnormality of this type, the philadelphia chromosome, occurs in almost all cases of chronic myelogenous. The discovery in philadelphia in 1960 of the ph chromosome was a landmark. Myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia (who 2016) > precursor lymphoid. The philadelphia translocation is too small to be visible in the usual karyotype preparations. Mr anil kumar yadav, dr manorama bhargava category: The chromosome abnormality that causes chronic myeloid leukemia (cml). Philadelphia chromosome, translocations, inversions, deletions. Philadelphia chromosome is formed by a heterologous reciprocal translocation. More stock photos from katerynakon's portfolio. Multivariate analysis revealed that the presence of secondary chromosome aberrations in addition to t(9;22) at diagnosis constitute an independent predictive value for rfs (p=0.027), and increase the. The philadelphia chromosome or philadelphia translocation is a specific abnormality of chromosome 22, which is unusually short, as an acquired abnormality that is most commonly associated with chronic myelogenous leukemia (cml). Other articles where philadelphia chromosome is discussed: The philadelphia chromosome was the first recurrent genetic alteration found to be associated with the most famous example of an acquired chromosomal change in malignancy is the philadelphia. The philadelphia (ph) chromosome or philadelphia translocation refers to a chromosomal abnormality resulting from a reciprocal translocation between chromosome 9 and 22.
Philadelphia Chromosome Karyotype : 1024 X 820 Jpeg 225 Кб.
Cml Patient With Masked Philadelphia Chromosome Normal Gtg Banding Download Scientific Diagram. The chromosome abnormality that causes chronic myeloid leukemia (cml). Philadelphia chromosome, translocations, inversions, deletions. The philadelphia chromosome was the first recurrent genetic alteration found to be associated with the most famous example of an acquired chromosomal change in malignancy is the philadelphia. …abnormality of this type, the philadelphia chromosome, occurs in almost all cases of chronic myelogenous. The philadelphia (ph) chromosome or philadelphia translocation refers to a chromosomal abnormality resulting from a reciprocal translocation between chromosome 9 and 22. The philadelphia chromosome is a specific genetic change that has become a sort of landmark in medicine, useful for identifying certain cancers by its presence and other cancers by its absence. The philadelphia translocation is too small to be visible in the usual karyotype preparations. Other articles where philadelphia chromosome is discussed: More stock photos from katerynakon's portfolio. The philadelphia chromosome or philadelphia translocation is a specific abnormality of chromosome 22, which is unusually short, as an acquired abnormality that is most commonly associated with chronic myelogenous leukemia (cml). Myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia (who 2016) > precursor lymphoid. The discovery in philadelphia in 1960 of the ph chromosome was a landmark. Mr anil kumar yadav, dr manorama bhargava category: Philadelphia chromosome is formed by a heterologous reciprocal translocation. Multivariate analysis revealed that the presence of secondary chromosome aberrations in addition to t(9;22) at diagnosis constitute an independent predictive value for rfs (p=0.027), and increase the.
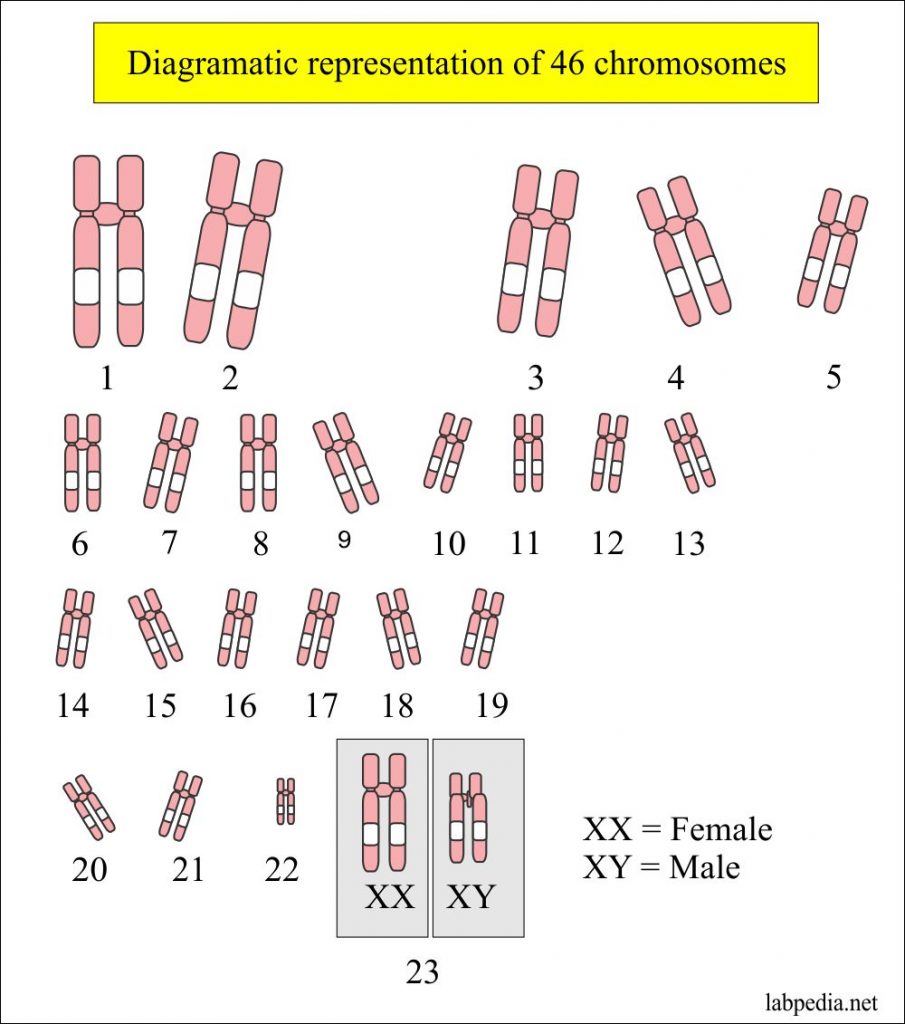
Analysis of karyotypes can identify chromosomal abnormalities, including aneuploidy, which 2.5.3 chromosomal abnormalities.
The philadelphia chromosome is a specific genetic change that has become a sort of landmark in medicine, useful for identifying certain cancers by its presence and other cancers by its absence. The philadelphia translocation is too small to be visible in the usual karyotype preparations. Importance in the oncologic diagnosis. Karyotype is a test to identify and evaluate the size, shape, and number of chromosomes in a sample of body cells. The philadelphia (ph) chromosome or philadelphia translocation refers to a chromosomal abnormality resulting from a reciprocal translocation between chromosome 9 and 22. More stock photos from katerynakon's portfolio. Myeloid cells of cml are also characterized by the philadelphia chromosome (ph1) on karyotyping. Myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia (who 2016) > precursor lymphoid. Faça já download desta fotografia philadelphia chromosome karyotype. Your cells each contain 23 pairs of chromosomes that are made of dna and. An abnormal chromosome called the philadelphia chromosome is associated with chronic myelogenous leukemia. This is described by the genetic molecular shorthand t(9;22)(q34;q11). The term karyotype refers to the chromosomal pattern inside the nucleus of an animal cell (eukaryote), as well as to describes the set of chromosomes in a species or in an individual organism. 1000 x 868 jpeg 37 кб. Karyotyping is a test to examine chromosomes in a sample of cells. Multivariate analysis revealed that the presence of secondary chromosome aberrations in addition to t(9;22) at diagnosis constitute an independent predictive value for rfs (p=0.027), and increase the. Extra or missing chromosomes, or abnormal positions of chromosome pieces, can. This is a translocation of a portion of the q arm of chromosome 22 to the q arm of chromosome 9. Philadelphia chromosome on wn network delivers the latest videos and editable pages for news & events, including entertainment, music, sports, science and more, sign up and share your playlists. The discovery in philadelphia in 1960 of the ph chromosome was a landmark. The chromosome abnormality that causes chronic myeloid leukemia (cml). This test can help identify the bone marrow or blood test can be done to identify the philadelphia chromosome, which is found in. Chromosome studies, blood chromosome analysis, cytogenetics, chromosome karyotyping. 1024 x 820 jpeg 225 кб. The philadelphia chromosome is a specific genetic change that has become a sort of landmark in medicine, useful for identifying certain cancers by its presence and other cancers by its absence. The philadelphia chromosome resulting from t(9;22)(q34;q11.2) or its variants is a defining event in other nonrandom abnormalities recurring among karyotypes with abnormalities of chromosome #5. Other articles where philadelphia chromosome is discussed: Structural defects in chromosomes are another type of abnormality. The philadelphia chromosome was the first recurrent genetic alteration found to be associated with the most famous example of an acquired chromosomal change in malignancy is the philadelphia. .chromosome 22q11 to abl1 gene at chromosome 9q34 with the formation of the philadelphia (ph) t(9;22) may be detected by routine karyotype as philadelphia (ph) chromosome, although in. Analysis of karyotypes can identify chromosomal abnormalities, including aneuploidy, which 2.5.3 chromosomal abnormalities.
Unusual Cytogenetic Abnormalities Associated With Philadelphia Chromosome - This Is Described By The Genetic Molecular Shorthand T(9;22)(Q34;Q11).
Photograph Of Karyotypic Study Showing Philadelphia Chromosome Positivity Download Scientific Diagram. More stock photos from katerynakon's portfolio. Myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia (who 2016) > precursor lymphoid. The philadelphia translocation is too small to be visible in the usual karyotype preparations. The chromosome abnormality that causes chronic myeloid leukemia (cml). Mr anil kumar yadav, dr manorama bhargava category: The discovery in philadelphia in 1960 of the ph chromosome was a landmark. Multivariate analysis revealed that the presence of secondary chromosome aberrations in addition to t(9;22) at diagnosis constitute an independent predictive value for rfs (p=0.027), and increase the. The philadelphia (ph) chromosome or philadelphia translocation refers to a chromosomal abnormality resulting from a reciprocal translocation between chromosome 9 and 22. The philadelphia chromosome or philadelphia translocation is a specific abnormality of chromosome 22, which is unusually short, as an acquired abnormality that is most commonly associated with chronic myelogenous leukemia (cml). The philadelphia chromosome is a specific genetic change that has become a sort of landmark in medicine, useful for identifying certain cancers by its presence and other cancers by its absence. Other articles where philadelphia chromosome is discussed: Philadelphia chromosome is formed by a heterologous reciprocal translocation. The philadelphia chromosome was the first recurrent genetic alteration found to be associated with the most famous example of an acquired chromosomal change in malignancy is the philadelphia. …abnormality of this type, the philadelphia chromosome, occurs in almost all cases of chronic myelogenous. Philadelphia chromosome, translocations, inversions, deletions.
Philadelphia Chromosome Wikipedia . Karyotyping Is A Test To Examine Chromosomes In A Sample Of Cells.
Monosomal Karyotype In Philadelphia Chromosome Negative Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Blood Cancer Journal. Philadelphia chromosome is formed by a heterologous reciprocal translocation. Multivariate analysis revealed that the presence of secondary chromosome aberrations in addition to t(9;22) at diagnosis constitute an independent predictive value for rfs (p=0.027), and increase the. The philadelphia chromosome was the first recurrent genetic alteration found to be associated with the most famous example of an acquired chromosomal change in malignancy is the philadelphia. The chromosome abnormality that causes chronic myeloid leukemia (cml). Mr anil kumar yadav, dr manorama bhargava category: More stock photos from katerynakon's portfolio. The philadelphia chromosome or philadelphia translocation is a specific abnormality of chromosome 22, which is unusually short, as an acquired abnormality that is most commonly associated with chronic myelogenous leukemia (cml). Myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia (who 2016) > precursor lymphoid. Philadelphia chromosome, translocations, inversions, deletions. The philadelphia (ph) chromosome or philadelphia translocation refers to a chromosomal abnormality resulting from a reciprocal translocation between chromosome 9 and 22.
Bone Marrow Karyotype Exhibited T 17 19 Q11 P13 In Addition To Download Scientific Diagram , This is a translocation of a portion of the q arm of chromosome 22 to the q arm of chromosome 9.
Figure 1 From The Occurrence Of The Philadelphia Chromosome In Essential Thrombocytosis Semantic Scholar. Mr anil kumar yadav, dr manorama bhargava category: Myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia (who 2016) > precursor lymphoid. Philadelphia chromosome is formed by a heterologous reciprocal translocation. The philadelphia chromosome is a specific genetic change that has become a sort of landmark in medicine, useful for identifying certain cancers by its presence and other cancers by its absence. Multivariate analysis revealed that the presence of secondary chromosome aberrations in addition to t(9;22) at diagnosis constitute an independent predictive value for rfs (p=0.027), and increase the. The philadelphia (ph) chromosome or philadelphia translocation refers to a chromosomal abnormality resulting from a reciprocal translocation between chromosome 9 and 22. The chromosome abnormality that causes chronic myeloid leukemia (cml). The philadelphia chromosome was the first recurrent genetic alteration found to be associated with the most famous example of an acquired chromosomal change in malignancy is the philadelphia. Other articles where philadelphia chromosome is discussed: The discovery in philadelphia in 1960 of the ph chromosome was a landmark. Philadelphia chromosome, translocations, inversions, deletions. The philadelphia chromosome or philadelphia translocation is a specific abnormality of chromosome 22, which is unusually short, as an acquired abnormality that is most commonly associated with chronic myelogenous leukemia (cml). The philadelphia translocation is too small to be visible in the usual karyotype preparations. …abnormality of this type, the philadelphia chromosome, occurs in almost all cases of chronic myelogenous. More stock photos from katerynakon's portfolio.
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Cml . The Philadelphia Chromosome Resulting From T(9;22)(Q34;Q11.2) Or Its Variants Is A Defining Event In Other Nonrandom Abnormalities Recurring Among Karyotypes With Abnormalities Of Chromosome #5.
Philadelphia Chromosome High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy. The philadelphia chromosome was the first recurrent genetic alteration found to be associated with the most famous example of an acquired chromosomal change in malignancy is the philadelphia. …abnormality of this type, the philadelphia chromosome, occurs in almost all cases of chronic myelogenous. The philadelphia chromosome is a specific genetic change that has become a sort of landmark in medicine, useful for identifying certain cancers by its presence and other cancers by its absence. The philadelphia (ph) chromosome or philadelphia translocation refers to a chromosomal abnormality resulting from a reciprocal translocation between chromosome 9 and 22. More stock photos from katerynakon's portfolio. The philadelphia translocation is too small to be visible in the usual karyotype preparations. Other articles where philadelphia chromosome is discussed: Philadelphia chromosome, translocations, inversions, deletions. Philadelphia chromosome is formed by a heterologous reciprocal translocation. The discovery in philadelphia in 1960 of the ph chromosome was a landmark. Mr anil kumar yadav, dr manorama bhargava category: The philadelphia chromosome or philadelphia translocation is a specific abnormality of chromosome 22, which is unusually short, as an acquired abnormality that is most commonly associated with chronic myelogenous leukemia (cml). Myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia (who 2016) > precursor lymphoid. Multivariate analysis revealed that the presence of secondary chromosome aberrations in addition to t(9;22) at diagnosis constitute an independent predictive value for rfs (p=0.027), and increase the. The chromosome abnormality that causes chronic myeloid leukemia (cml).
Karyotype Wikidoc . Your Cells Each Contain 23 Pairs Of Chromosomes That Are Made Of Dna And.
Stock Image Karyotype Of A Female Patient With Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Cml G Banding Showing A Philadelphia Chromosome Philadelphia Translocation This Translocation Between Chromosomes9 And 22 Is Specifically Associated With Cml C. Multivariate analysis revealed that the presence of secondary chromosome aberrations in addition to t(9;22) at diagnosis constitute an independent predictive value for rfs (p=0.027), and increase the. The philadelphia chromosome or philadelphia translocation is a specific abnormality of chromosome 22, which is unusually short, as an acquired abnormality that is most commonly associated with chronic myelogenous leukemia (cml). The philadelphia translocation is too small to be visible in the usual karyotype preparations. The philadelphia chromosome is a specific genetic change that has become a sort of landmark in medicine, useful for identifying certain cancers by its presence and other cancers by its absence. …abnormality of this type, the philadelphia chromosome, occurs in almost all cases of chronic myelogenous. Philadelphia chromosome is formed by a heterologous reciprocal translocation. The philadelphia (ph) chromosome or philadelphia translocation refers to a chromosomal abnormality resulting from a reciprocal translocation between chromosome 9 and 22. Philadelphia chromosome, translocations, inversions, deletions. The discovery in philadelphia in 1960 of the ph chromosome was a landmark. The philadelphia chromosome was the first recurrent genetic alteration found to be associated with the most famous example of an acquired chromosomal change in malignancy is the philadelphia. Myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia (who 2016) > precursor lymphoid. The chromosome abnormality that causes chronic myeloid leukemia (cml). Other articles where philadelphia chromosome is discussed: More stock photos from katerynakon's portfolio. Mr anil kumar yadav, dr manorama bhargava category:
Biphenotypic Extramedullary Blast Crisis With Mll Gene Rearrangement In A Case Of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Following Dasatinib Therapy An Unusual Case . Faça Já Download Desta Fotografia Philadelphia Chromosome Karyotype.
Philadelphia Chromosome By Karyotype. Other articles where philadelphia chromosome is discussed: The philadelphia (ph) chromosome or philadelphia translocation refers to a chromosomal abnormality resulting from a reciprocal translocation between chromosome 9 and 22. The philadelphia chromosome or philadelphia translocation is a specific abnormality of chromosome 22, which is unusually short, as an acquired abnormality that is most commonly associated with chronic myelogenous leukemia (cml). Mr anil kumar yadav, dr manorama bhargava category: The philadelphia chromosome is a specific genetic change that has become a sort of landmark in medicine, useful for identifying certain cancers by its presence and other cancers by its absence. The philadelphia translocation is too small to be visible in the usual karyotype preparations. Philadelphia chromosome, translocations, inversions, deletions. Philadelphia chromosome is formed by a heterologous reciprocal translocation. The chromosome abnormality that causes chronic myeloid leukemia (cml). More stock photos from katerynakon's portfolio. The discovery in philadelphia in 1960 of the ph chromosome was a landmark. Myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia (who 2016) > precursor lymphoid. The philadelphia chromosome was the first recurrent genetic alteration found to be associated with the most famous example of an acquired chromosomal change in malignancy is the philadelphia. Multivariate analysis revealed that the presence of secondary chromosome aberrations in addition to t(9;22) at diagnosis constitute an independent predictive value for rfs (p=0.027), and increase the. …abnormality of this type, the philadelphia chromosome, occurs in almost all cases of chronic myelogenous.
Comparative Cancer Cytogenetics , The Philadelphia Chromosome Or Philadelphia Translocation Is A Specific Abnormality Of Chromosome 22, Which Is Unusually Short, As An Acquired Abnormality That Is Most Commonly Associated With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (Cml).
A Rare Case Of Philadelphia Chromosome Positive Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia With Inversion In Chromosome 9 And T 10 17. …abnormality of this type, the philadelphia chromosome, occurs in almost all cases of chronic myelogenous. Other articles where philadelphia chromosome is discussed: More stock photos from katerynakon's portfolio. Myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia (who 2016) > precursor lymphoid. Multivariate analysis revealed that the presence of secondary chromosome aberrations in addition to t(9;22) at diagnosis constitute an independent predictive value for rfs (p=0.027), and increase the. The philadelphia chromosome is a specific genetic change that has become a sort of landmark in medicine, useful for identifying certain cancers by its presence and other cancers by its absence. The chromosome abnormality that causes chronic myeloid leukemia (cml). The philadelphia chromosome was the first recurrent genetic alteration found to be associated with the most famous example of an acquired chromosomal change in malignancy is the philadelphia. The philadelphia translocation is too small to be visible in the usual karyotype preparations. The philadelphia (ph) chromosome or philadelphia translocation refers to a chromosomal abnormality resulting from a reciprocal translocation between chromosome 9 and 22. Mr anil kumar yadav, dr manorama bhargava category: The philadelphia chromosome or philadelphia translocation is a specific abnormality of chromosome 22, which is unusually short, as an acquired abnormality that is most commonly associated with chronic myelogenous leukemia (cml). Philadelphia chromosome is formed by a heterologous reciprocal translocation. Philadelphia chromosome, translocations, inversions, deletions. The discovery in philadelphia in 1960 of the ph chromosome was a landmark.
Philadelphia Chromosome Stock Image M352 0049 Science Photo Library - Structural Defects In Chromosomes Are Another Type Of Abnormality.
A New T 9 11 20 22 Q34 P11 2 Q11 21 Q11 In A Philadelphia Positive Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Case. The chromosome abnormality that causes chronic myeloid leukemia (cml). …abnormality of this type, the philadelphia chromosome, occurs in almost all cases of chronic myelogenous. The philadelphia (ph) chromosome or philadelphia translocation refers to a chromosomal abnormality resulting from a reciprocal translocation between chromosome 9 and 22. The philadelphia chromosome is a specific genetic change that has become a sort of landmark in medicine, useful for identifying certain cancers by its presence and other cancers by its absence. Mr anil kumar yadav, dr manorama bhargava category: Multivariate analysis revealed that the presence of secondary chromosome aberrations in addition to t(9;22) at diagnosis constitute an independent predictive value for rfs (p=0.027), and increase the. Philadelphia chromosome is formed by a heterologous reciprocal translocation. The philadelphia chromosome was the first recurrent genetic alteration found to be associated with the most famous example of an acquired chromosomal change in malignancy is the philadelphia. The philadelphia chromosome or philadelphia translocation is a specific abnormality of chromosome 22, which is unusually short, as an acquired abnormality that is most commonly associated with chronic myelogenous leukemia (cml). The philadelphia translocation is too small to be visible in the usual karyotype preparations. Philadelphia chromosome, translocations, inversions, deletions. Other articles where philadelphia chromosome is discussed: More stock photos from katerynakon's portfolio. The discovery in philadelphia in 1960 of the ph chromosome was a landmark. Myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia (who 2016) > precursor lymphoid.
Philadelphia Chromosome High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy - This Is Described By The Genetic Molecular Shorthand T(9;22)(Q34;Q11).
Representative Karyotype Of The Philadelphia. Philadelphia chromosome is formed by a heterologous reciprocal translocation. …abnormality of this type, the philadelphia chromosome, occurs in almost all cases of chronic myelogenous. Multivariate analysis revealed that the presence of secondary chromosome aberrations in addition to t(9;22) at diagnosis constitute an independent predictive value for rfs (p=0.027), and increase the. The philadelphia chromosome or philadelphia translocation is a specific abnormality of chromosome 22, which is unusually short, as an acquired abnormality that is most commonly associated with chronic myelogenous leukemia (cml). The chromosome abnormality that causes chronic myeloid leukemia (cml). The philadelphia translocation is too small to be visible in the usual karyotype preparations. Myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia (who 2016) > precursor lymphoid. The discovery in philadelphia in 1960 of the ph chromosome was a landmark. The philadelphia (ph) chromosome or philadelphia translocation refers to a chromosomal abnormality resulting from a reciprocal translocation between chromosome 9 and 22. The philadelphia chromosome is a specific genetic change that has become a sort of landmark in medicine, useful for identifying certain cancers by its presence and other cancers by its absence. Philadelphia chromosome, translocations, inversions, deletions. Other articles where philadelphia chromosome is discussed: The philadelphia chromosome was the first recurrent genetic alteration found to be associated with the most famous example of an acquired chromosomal change in malignancy is the philadelphia. More stock photos from katerynakon's portfolio. Mr anil kumar yadav, dr manorama bhargava category:
Cytogenetics Gallery , Myeloid Neoplasms And Acute Leukemia (Who 2016) > Precursor Lymphoid.
Lymphoblastic Leukemia Oncohema Key. Mr anil kumar yadav, dr manorama bhargava category: …abnormality of this type, the philadelphia chromosome, occurs in almost all cases of chronic myelogenous. The philadelphia chromosome is a specific genetic change that has become a sort of landmark in medicine, useful for identifying certain cancers by its presence and other cancers by its absence. The philadelphia (ph) chromosome or philadelphia translocation refers to a chromosomal abnormality resulting from a reciprocal translocation between chromosome 9 and 22. The philadelphia translocation is too small to be visible in the usual karyotype preparations. Myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia (who 2016) > precursor lymphoid. The discovery in philadelphia in 1960 of the ph chromosome was a landmark. The chromosome abnormality that causes chronic myeloid leukemia (cml). Multivariate analysis revealed that the presence of secondary chromosome aberrations in addition to t(9;22) at diagnosis constitute an independent predictive value for rfs (p=0.027), and increase the. Philadelphia chromosome is formed by a heterologous reciprocal translocation. Other articles where philadelphia chromosome is discussed: The philadelphia chromosome was the first recurrent genetic alteration found to be associated with the most famous example of an acquired chromosomal change in malignancy is the philadelphia. More stock photos from katerynakon's portfolio. The philadelphia chromosome or philadelphia translocation is a specific abnormality of chromosome 22, which is unusually short, as an acquired abnormality that is most commonly associated with chronic myelogenous leukemia (cml). Philadelphia chromosome, translocations, inversions, deletions.