Merkel Cell Carcinoma Histology. The tumour is centered in the dermis with frequent involvement of the overlying epidermis (figures 1, 2) and may invade the subcutaneous fat. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) of the skin is a rare, aggressive, cutaneous malignancy that predominantly affects older adults with light skin types and has a merkel cell carcinoma: It is also known as cutaneous apudoma, primary neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin, primary small cell carcinoma of the skin. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare but aggressive neuroendocrine tumour of the skin with high rate of local recurrence and distant metastatic potential leading to poor outcomes. The tumour forms sheets, nests and rarely ribbons. Merkel cells are normally found as innervated clusters of cells around hair follicles in the basal layer of the epidermis and are. Diagnosis requires microscopic evaluation as the clinical appearance is nonspecific and can mimic a variety of benign and malignant skin lesions. Merkel cell carcinoma most often develops in older people. Merkel cell carcinoma treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Since the first description of the merkel cell carcinoma by cyril toker in 1972, the number of studies has significantly increased over the last 4 decades. Merkel cell carcinoma is a neuroendocrine carcinoma composed of densely blue cells. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is an uncommon and aggressive cutaneous neoplasm that lacks distinguishing clinical features. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare and aggressive skin cancer occurring in about 3 people per 1,000,000 members of the population. Get detailed information about the diagnosis and treatment of newly diagnosed and recurrent merkel cell carcinoma in this summary for clinicians. Merkel cell carcinoma is a highly aggressive primary cutaneous neuroendocrine carcinoma primarily affecting elderly and immunosuppressed individuals.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma Histology - Merkel Cell Carcinoma (Mcc) Is An Uncommon And Aggressive Cutaneous Neoplasm That Lacks Distinguishing Clinical Features.
Advances In Merkel Cell Carcinoma From A Pathologist S Perspective Sciencedirect. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) of the skin is a rare, aggressive, cutaneous malignancy that predominantly affects older adults with light skin types and has a merkel cell carcinoma: Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is an uncommon and aggressive cutaneous neoplasm that lacks distinguishing clinical features. Merkel cell carcinoma is a neuroendocrine carcinoma composed of densely blue cells. The tumour is centered in the dermis with frequent involvement of the overlying epidermis (figures 1, 2) and may invade the subcutaneous fat. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare but aggressive neuroendocrine tumour of the skin with high rate of local recurrence and distant metastatic potential leading to poor outcomes. Get detailed information about the diagnosis and treatment of newly diagnosed and recurrent merkel cell carcinoma in this summary for clinicians. Since the first description of the merkel cell carcinoma by cyril toker in 1972, the number of studies has significantly increased over the last 4 decades. Merkel cell carcinoma is a highly aggressive primary cutaneous neuroendocrine carcinoma primarily affecting elderly and immunosuppressed individuals. Merkel cells are normally found as innervated clusters of cells around hair follicles in the basal layer of the epidermis and are. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare and aggressive skin cancer occurring in about 3 people per 1,000,000 members of the population. Merkel cell carcinoma most often develops in older people. Diagnosis requires microscopic evaluation as the clinical appearance is nonspecific and can mimic a variety of benign and malignant skin lesions. It is also known as cutaneous apudoma, primary neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin, primary small cell carcinoma of the skin. Merkel cell carcinoma treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. The tumour forms sheets, nests and rarely ribbons.
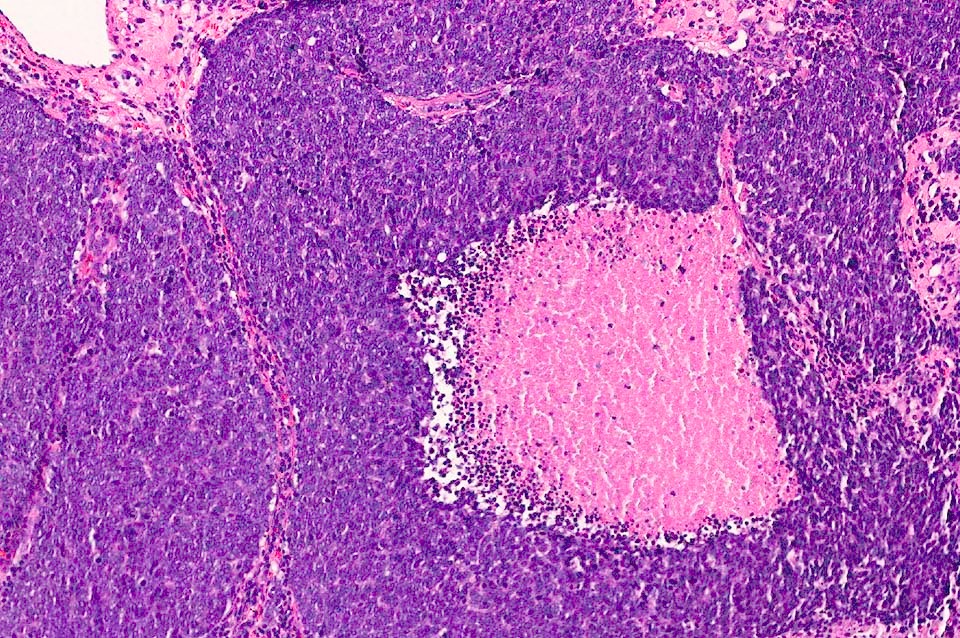
Merkel cell carcinoma is different from other skin cancers in that it does not have a common identifiable trait across all cases.
Click here for the consumer version. An overview of merkel cells, merkel cell carcinoma, symptoms, and causes. The tumour forms sheets, nests and rarely ribbons. Merkel cells were first described in the late 1800s by a german doctor named friedrich merkel. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare, aggressive form of skin cancer with a high risk for returning (recurring) and spreading (metastasizing), often within two to three years after initial diagnosis. Click here for the consumer version. Merkel cell carcinoma is different from other skin cancers in that it does not have a common identifiable trait across all cases. Identified merkel cell polyomavirus (mcpyv) integration into the host genome as the main event. The cell of origin in mcc might be the pro/pre b cell rather than the merkel cell (zur hausen, cancer res 2013). Merkel cell carcinoma is a neuroendocrine carcinoma composed of densely blue cells. It's a type of skin cancer that occurs when cells in the skin, known as merkel cells, grow uncontrollably. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) of the skin is a rare, aggressive, cutaneous malignancy that predominantly affects older adults with light skin types and has a merkel cell carcinoma: Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is an uncommon and aggressive cutaneous neoplasm that lacks distinguishing clinical features. Merkel cell carcinoma forms on or just beneath the skin. A rare disease in which cancer cells form in the skin. Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare, but highly malignant tumor of the skin with high rates of metastasis and poor survival. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a primary neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin. Merkel cell carcinoma, also called neuroendocrine cancer of the skin, is an aggressive type of skin cancer that affects only about 400 people in the with early detection and treatment, merkel cell carcinoma can be well contained and even cured. Current us incidence and projected increases based on changing demographics. Treatment becomes more difficult as the tumor. Its incidence rate rises and is currently about.6/100000/year. Merkel cell carcinoma typically occurs in elderly fair skinned individuals in the seventh and eighth decades of life, with a slight male predilection. Mcc is a fatal disease, and patients have the histology of mcc is typical of small round blue cell tumours, an entity that includes a wide variety of highly malignant tumours: Merkel cells, found in the top layer of the skin, are very close to the. The ewing family of tumours, olfactory. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare type of skin cancer. Diagnosis requires microscopic evaluation as the clinical appearance is nonspecific and can mimic a variety of benign and malignant skin lesions. Merkel cell carcinoma most often develops in older people. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is an aggressive cutaneous neuroendocrine tumor. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare but aggressive neuroendocrine tumour of the skin with high rate of local recurrence and distant metastatic potential leading to poor outcomes. Learn about merkel cell carcinoma and find information on how we support and care for people merkel cell carcinoma:
Pathology Outlines Merkel Cell Carcinoma : Diagnosis Requires Microscopic Evaluation As The Clinical Appearance Is Nonspecific And Can Mimic A Variety Of Benign And Malignant Skin Lesions.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Wikipedia. Diagnosis requires microscopic evaluation as the clinical appearance is nonspecific and can mimic a variety of benign and malignant skin lesions. The tumour forms sheets, nests and rarely ribbons. It is also known as cutaneous apudoma, primary neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin, primary small cell carcinoma of the skin. Merkel cell carcinoma is a highly aggressive primary cutaneous neuroendocrine carcinoma primarily affecting elderly and immunosuppressed individuals. Merkel cell carcinoma most often develops in older people. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare but aggressive neuroendocrine tumour of the skin with high rate of local recurrence and distant metastatic potential leading to poor outcomes. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) of the skin is a rare, aggressive, cutaneous malignancy that predominantly affects older adults with light skin types and has a merkel cell carcinoma: The tumour is centered in the dermis with frequent involvement of the overlying epidermis (figures 1, 2) and may invade the subcutaneous fat. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare and aggressive skin cancer occurring in about 3 people per 1,000,000 members of the population. Get detailed information about the diagnosis and treatment of newly diagnosed and recurrent merkel cell carcinoma in this summary for clinicians. Merkel cells are normally found as innervated clusters of cells around hair follicles in the basal layer of the epidermis and are. Since the first description of the merkel cell carcinoma by cyril toker in 1972, the number of studies has significantly increased over the last 4 decades. Merkel cell carcinoma is a neuroendocrine carcinoma composed of densely blue cells. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is an uncommon and aggressive cutaneous neoplasm that lacks distinguishing clinical features. Merkel cell carcinoma treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
Frontiers Histogenesis Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma A Comprehensive Review Oncology , Mcc Is A Fatal Disease, And Patients Have The Histology Of Mcc Is Typical Of Small Round Blue Cell Tumours, An Entity That Includes A Wide Variety Of Highly Malignant Tumours:
Pathophysiology Of Merkel Cell Munde Pb Khandekar Sp Dive Aa Sharma A J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. Merkel cells are normally found as innervated clusters of cells around hair follicles in the basal layer of the epidermis and are. It is also known as cutaneous apudoma, primary neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin, primary small cell carcinoma of the skin. Diagnosis requires microscopic evaluation as the clinical appearance is nonspecific and can mimic a variety of benign and malignant skin lesions. Since the first description of the merkel cell carcinoma by cyril toker in 1972, the number of studies has significantly increased over the last 4 decades. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare but aggressive neuroendocrine tumour of the skin with high rate of local recurrence and distant metastatic potential leading to poor outcomes. Merkel cell carcinoma is a highly aggressive primary cutaneous neuroendocrine carcinoma primarily affecting elderly and immunosuppressed individuals. Merkel cell carcinoma treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Get detailed information about the diagnosis and treatment of newly diagnosed and recurrent merkel cell carcinoma in this summary for clinicians. The tumour forms sheets, nests and rarely ribbons. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare and aggressive skin cancer occurring in about 3 people per 1,000,000 members of the population.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma Treatment Pdq Health Professional Version National Cancer Institute . Merkel cell carcinoma, also called neuroendocrine cancer of the skin, is an aggressive type of skin cancer that affects only about 400 people in the with early detection and treatment, merkel cell carcinoma can be well contained and even cured.
Case Of The Month May 2019 Cedars Sinai. Diagnosis requires microscopic evaluation as the clinical appearance is nonspecific and can mimic a variety of benign and malignant skin lesions. Merkel cell carcinoma treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Merkel cell carcinoma is a neuroendocrine carcinoma composed of densely blue cells. The tumour forms sheets, nests and rarely ribbons. Since the first description of the merkel cell carcinoma by cyril toker in 1972, the number of studies has significantly increased over the last 4 decades. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is an uncommon and aggressive cutaneous neoplasm that lacks distinguishing clinical features. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) of the skin is a rare, aggressive, cutaneous malignancy that predominantly affects older adults with light skin types and has a merkel cell carcinoma: Get detailed information about the diagnosis and treatment of newly diagnosed and recurrent merkel cell carcinoma in this summary for clinicians. Merkel cell carcinoma most often develops in older people. Merkel cells are normally found as innervated clusters of cells around hair follicles in the basal layer of the epidermis and are. Merkel cell carcinoma is a highly aggressive primary cutaneous neuroendocrine carcinoma primarily affecting elderly and immunosuppressed individuals. The tumour is centered in the dermis with frequent involvement of the overlying epidermis (figures 1, 2) and may invade the subcutaneous fat. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare but aggressive neuroendocrine tumour of the skin with high rate of local recurrence and distant metastatic potential leading to poor outcomes. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare and aggressive skin cancer occurring in about 3 people per 1,000,000 members of the population. It is also known as cutaneous apudoma, primary neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin, primary small cell carcinoma of the skin.
Dermatopathology 101 Part 2 Skin Tumors Liersch 2017 Jddg Journal Der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft Wiley Online Library - Since The First Description Of The Merkel Cell Carcinoma By Cyril Toker In 1972, The Number Of Studies Has Significantly Increased Over The Last 4 Decades.
Hematoxylin And Eosin Slide 2 10 Merkel Cell Carcinoma Notes Dermal Download Scientific Diagram. It is also known as cutaneous apudoma, primary neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin, primary small cell carcinoma of the skin. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) of the skin is a rare, aggressive, cutaneous malignancy that predominantly affects older adults with light skin types and has a merkel cell carcinoma: The tumour forms sheets, nests and rarely ribbons. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is an uncommon and aggressive cutaneous neoplasm that lacks distinguishing clinical features. Diagnosis requires microscopic evaluation as the clinical appearance is nonspecific and can mimic a variety of benign and malignant skin lesions. Merkel cell carcinoma treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Merkel cell carcinoma is a highly aggressive primary cutaneous neuroendocrine carcinoma primarily affecting elderly and immunosuppressed individuals. Merkel cell carcinoma is a neuroendocrine carcinoma composed of densely blue cells. Merkel cells are normally found as innervated clusters of cells around hair follicles in the basal layer of the epidermis and are. Get detailed information about the diagnosis and treatment of newly diagnosed and recurrent merkel cell carcinoma in this summary for clinicians. The tumour is centered in the dermis with frequent involvement of the overlying epidermis (figures 1, 2) and may invade the subcutaneous fat. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare and aggressive skin cancer occurring in about 3 people per 1,000,000 members of the population. Since the first description of the merkel cell carcinoma by cyril toker in 1972, the number of studies has significantly increased over the last 4 decades. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare but aggressive neuroendocrine tumour of the skin with high rate of local recurrence and distant metastatic potential leading to poor outcomes. Merkel cell carcinoma most often develops in older people.
Merkel Cell . Merkel Cells Were First Described In The Late 1800S By A German Doctor Named Friedrich Merkel.
Advances In Merkel Cell Carcinoma From A Pathologist S Perspective Sciencedirect. Merkel cell carcinoma is a neuroendocrine carcinoma composed of densely blue cells. It is also known as cutaneous apudoma, primary neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin, primary small cell carcinoma of the skin. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare but aggressive neuroendocrine tumour of the skin with high rate of local recurrence and distant metastatic potential leading to poor outcomes. Merkel cell carcinoma treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Diagnosis requires microscopic evaluation as the clinical appearance is nonspecific and can mimic a variety of benign and malignant skin lesions. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) of the skin is a rare, aggressive, cutaneous malignancy that predominantly affects older adults with light skin types and has a merkel cell carcinoma: Get detailed information about the diagnosis and treatment of newly diagnosed and recurrent merkel cell carcinoma in this summary for clinicians. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is an uncommon and aggressive cutaneous neoplasm that lacks distinguishing clinical features. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare and aggressive skin cancer occurring in about 3 people per 1,000,000 members of the population. Merkel cells are normally found as innervated clusters of cells around hair follicles in the basal layer of the epidermis and are. Merkel cell carcinoma most often develops in older people. The tumour is centered in the dermis with frequent involvement of the overlying epidermis (figures 1, 2) and may invade the subcutaneous fat. The tumour forms sheets, nests and rarely ribbons. Since the first description of the merkel cell carcinoma by cyril toker in 1972, the number of studies has significantly increased over the last 4 decades. Merkel cell carcinoma is a highly aggressive primary cutaneous neuroendocrine carcinoma primarily affecting elderly and immunosuppressed individuals.
Malignant Lesions Of The External Periocular Tissues Tutorial : Merkel Cells Were First Described In The Late 1800S By A German Doctor Named Friedrich Merkel.
Cytokeratin 20 Negative Merkel Cell Carcinoma Is Infrequently Associated With The Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Modern Pathology. Merkel cell carcinoma is a highly aggressive primary cutaneous neuroendocrine carcinoma primarily affecting elderly and immunosuppressed individuals. Merkel cells are normally found as innervated clusters of cells around hair follicles in the basal layer of the epidermis and are. Merkel cell carcinoma most often develops in older people. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare and aggressive skin cancer occurring in about 3 people per 1,000,000 members of the population. Merkel cell carcinoma treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. The tumour is centered in the dermis with frequent involvement of the overlying epidermis (figures 1, 2) and may invade the subcutaneous fat. The tumour forms sheets, nests and rarely ribbons. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is an uncommon and aggressive cutaneous neoplasm that lacks distinguishing clinical features. Diagnosis requires microscopic evaluation as the clinical appearance is nonspecific and can mimic a variety of benign and malignant skin lesions. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) of the skin is a rare, aggressive, cutaneous malignancy that predominantly affects older adults with light skin types and has a merkel cell carcinoma: Since the first description of the merkel cell carcinoma by cyril toker in 1972, the number of studies has significantly increased over the last 4 decades. Get detailed information about the diagnosis and treatment of newly diagnosed and recurrent merkel cell carcinoma in this summary for clinicians. It is also known as cutaneous apudoma, primary neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin, primary small cell carcinoma of the skin. Merkel cell carcinoma is a neuroendocrine carcinoma composed of densely blue cells. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare but aggressive neuroendocrine tumour of the skin with high rate of local recurrence and distant metastatic potential leading to poor outcomes.
Pathology Outlines Merkel Cell Carcinoma . Clinical Differential Diagnoses Include Basal Cell Carcinoma, Cyst, Amelanotic Melanoma, Lymphoma And Atypical.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma And Metastatic And Sarcomatoid Carcinomas Involving Soft Tissue Chapter 29 Modern Soft Tissue Pathology. The tumour is centered in the dermis with frequent involvement of the overlying epidermis (figures 1, 2) and may invade the subcutaneous fat. Merkel cell carcinoma treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Since the first description of the merkel cell carcinoma by cyril toker in 1972, the number of studies has significantly increased over the last 4 decades. Merkel cell carcinoma is a highly aggressive primary cutaneous neuroendocrine carcinoma primarily affecting elderly and immunosuppressed individuals. Get detailed information about the diagnosis and treatment of newly diagnosed and recurrent merkel cell carcinoma in this summary for clinicians. Merkel cells are normally found as innervated clusters of cells around hair follicles in the basal layer of the epidermis and are. Diagnosis requires microscopic evaluation as the clinical appearance is nonspecific and can mimic a variety of benign and malignant skin lesions. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare but aggressive neuroendocrine tumour of the skin with high rate of local recurrence and distant metastatic potential leading to poor outcomes. The tumour forms sheets, nests and rarely ribbons. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) of the skin is a rare, aggressive, cutaneous malignancy that predominantly affects older adults with light skin types and has a merkel cell carcinoma: Merkel cell carcinoma most often develops in older people. It is also known as cutaneous apudoma, primary neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin, primary small cell carcinoma of the skin. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare and aggressive skin cancer occurring in about 3 people per 1,000,000 members of the population. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is an uncommon and aggressive cutaneous neoplasm that lacks distinguishing clinical features. Merkel cell carcinoma is a neuroendocrine carcinoma composed of densely blue cells.
Histology Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma From Patient In Figure 1 Showing The Download Scientific Diagram . Merkel Cell Carcinoma Is A Rare, But Highly Malignant Tumor Of The Skin With High Rates Of Metastasis And Poor Survival.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma With Seborrheic Keratosis A Unique Association Anand Ms Krishnamurthy S Ravindranath S Ranganathan J Indian J Pathol Microbiol. Merkel cell carcinoma is a neuroendocrine carcinoma composed of densely blue cells. Merkel cell carcinoma is a highly aggressive primary cutaneous neuroendocrine carcinoma primarily affecting elderly and immunosuppressed individuals. The tumour is centered in the dermis with frequent involvement of the overlying epidermis (figures 1, 2) and may invade the subcutaneous fat. Get detailed information about the diagnosis and treatment of newly diagnosed and recurrent merkel cell carcinoma in this summary for clinicians. Since the first description of the merkel cell carcinoma by cyril toker in 1972, the number of studies has significantly increased over the last 4 decades. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare but aggressive neuroendocrine tumour of the skin with high rate of local recurrence and distant metastatic potential leading to poor outcomes. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) of the skin is a rare, aggressive, cutaneous malignancy that predominantly affects older adults with light skin types and has a merkel cell carcinoma: Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare and aggressive skin cancer occurring in about 3 people per 1,000,000 members of the population. Merkel cell carcinoma treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. The tumour forms sheets, nests and rarely ribbons. Merkel cells are normally found as innervated clusters of cells around hair follicles in the basal layer of the epidermis and are. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is an uncommon and aggressive cutaneous neoplasm that lacks distinguishing clinical features. It is also known as cutaneous apudoma, primary neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin, primary small cell carcinoma of the skin. Diagnosis requires microscopic evaluation as the clinical appearance is nonspecific and can mimic a variety of benign and malignant skin lesions. Merkel cell carcinoma most often develops in older people.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma Skin Histology : Merkel Cell Carcinoma (Mcc) Is An Uncommon And Aggressive Cutaneous Neoplasm That Lacks Distinguishing Clinical Features.
Malignant Lesions Of The External Periocular Tissues Tutorial. Get detailed information about the diagnosis and treatment of newly diagnosed and recurrent merkel cell carcinoma in this summary for clinicians. Merkel cell carcinoma is a neuroendocrine carcinoma composed of densely blue cells. Merkel cell carcinoma is a highly aggressive primary cutaneous neuroendocrine carcinoma primarily affecting elderly and immunosuppressed individuals. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare and aggressive skin cancer occurring in about 3 people per 1,000,000 members of the population. The tumour forms sheets, nests and rarely ribbons. Since the first description of the merkel cell carcinoma by cyril toker in 1972, the number of studies has significantly increased over the last 4 decades. Diagnosis requires microscopic evaluation as the clinical appearance is nonspecific and can mimic a variety of benign and malignant skin lesions. The tumour is centered in the dermis with frequent involvement of the overlying epidermis (figures 1, 2) and may invade the subcutaneous fat. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is an uncommon and aggressive cutaneous neoplasm that lacks distinguishing clinical features. It is also known as cutaneous apudoma, primary neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin, primary small cell carcinoma of the skin. Merkel cells are normally found as innervated clusters of cells around hair follicles in the basal layer of the epidermis and are. Merkel cell carcinoma treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Merkel cell carcinoma most often develops in older people. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) of the skin is a rare, aggressive, cutaneous malignancy that predominantly affects older adults with light skin types and has a merkel cell carcinoma: Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare but aggressive neuroendocrine tumour of the skin with high rate of local recurrence and distant metastatic potential leading to poor outcomes.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Histology Health Pictures Basal Cell Carcinoma Basal Cell Health Pictures - Merkel Cell Carcinoma Treatment Options Include Surgery, Radiation Therapy, And Chemotherapy.
Researchers Unlock Keys To Staging And Risk Stratification Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma Consult Qd. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is an uncommon and aggressive cutaneous neoplasm that lacks distinguishing clinical features. Merkel cell carcinoma is a highly aggressive primary cutaneous neuroendocrine carcinoma primarily affecting elderly and immunosuppressed individuals. Get detailed information about the diagnosis and treatment of newly diagnosed and recurrent merkel cell carcinoma in this summary for clinicians. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare and aggressive skin cancer occurring in about 3 people per 1,000,000 members of the population. The tumour is centered in the dermis with frequent involvement of the overlying epidermis (figures 1, 2) and may invade the subcutaneous fat. Diagnosis requires microscopic evaluation as the clinical appearance is nonspecific and can mimic a variety of benign and malignant skin lesions. Merkel cells are normally found as innervated clusters of cells around hair follicles in the basal layer of the epidermis and are. Since the first description of the merkel cell carcinoma by cyril toker in 1972, the number of studies has significantly increased over the last 4 decades. It is also known as cutaneous apudoma, primary neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin, primary small cell carcinoma of the skin. Merkel cell carcinoma is a neuroendocrine carcinoma composed of densely blue cells. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) of the skin is a rare, aggressive, cutaneous malignancy that predominantly affects older adults with light skin types and has a merkel cell carcinoma: Merkel cell carcinoma most often develops in older people. Merkel cell carcinoma (mcc) is a rare but aggressive neuroendocrine tumour of the skin with high rate of local recurrence and distant metastatic potential leading to poor outcomes. Merkel cell carcinoma treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. The tumour forms sheets, nests and rarely ribbons.