Barrett's Esophagus Histology. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide.
Barrett's Esophagus Histology , Free Information About Barrett's Oesophagus.
Barrett S Esophagus 2. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food.
Risk factors for barrett's esophagus and esophageal cancer include having had severe gastroesophageal reflux disease for a long time, being male, and being overweight or obese.
The condition was first described in 1950 by. We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. Barrett esophagus (be) is a metaplastic replacement of the stratified squamous epithelium of the distal esophagus with columnar epithelium containing goblet cells. This occurs in the area where the. This article details information about symptoms, screening, diagnosis. Barrett esophagus is a term for intestinal metaplasia of the esophagus. It is believed to be due to severe, longstanding, gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). Barrett's esophagus, abbreviated be, is a relatively common pathology of the esophagus, that is associated with an increased risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis. © 2004 mayo foundation for medical education and research. In barrett's oesophagitis or barrett's oesophagus cells that line the lower gullet are abnormal. Summary • barrett's oesophagus is an endoscopic diagnosis corroborated by histology. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. Barrett's oesophagus refers to metaplasia of the oesophageal epithelial lining, whereby normal stratified squamous epithelium is replaced by simple columnar epithelium. Barrett's esophagus is a condition marked by an abnormality in the lining of the lower esophagus. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; Diagnosis is made by clinicans not pathologists. Haoxiang zhang, caifei shen, pu wang, ji feng, yin xu. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. Barrett's esophagus is a complication of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. Barrett's esophagus (be) is characterized as histologic evidence of intestinal metaplasia is pathogenesis of barrett s esophagus. The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. In barrett esophagus, healthy esophageal epithelium is replaced with metaplastic columnar cells—the result, it is believed, of damage from prolonged exposure of the esophagus to the refluxate of. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Risk factors for barrett's esophagus and esophageal cancer include having had severe gastroesophageal reflux disease for a long time, being male, and being overweight or obese. Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist.
Barrett S Esophagus , In This Third (# 3) Video Of Esophageal Histology, We Will Discuss About A Very Important Pathology:
Barrett S Esophagus And Esophageal Cancer An Overview. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux.
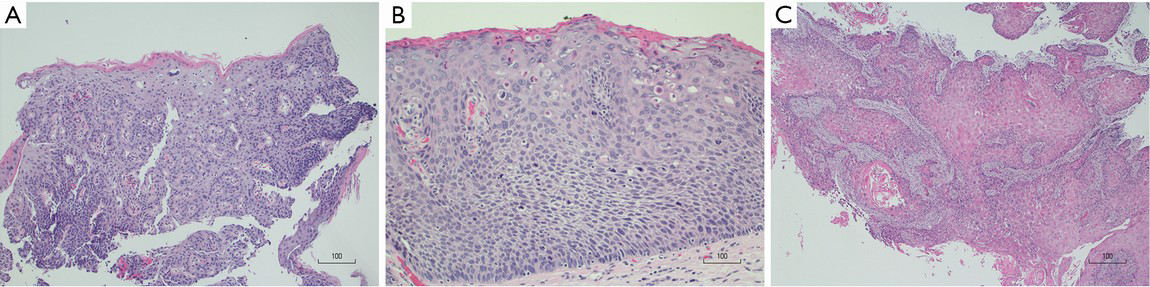
Gastrointestdisord Free Full Text Histopathology Of Barrett S Esophagus And Early Stage Esophageal Adenocarcinoma An Updated Review Html : In Barrett's Oesophagitis Or Barrett's Oesophagus Cells That Line The Lower Gullet Are Abnormal.
Increasing Diagnostic Accuracy To Grade Dysplasia In Barrett S Esophagus Using An Immunohistochemical Panel For Cdx2 P120ctn C Myc And Jagged1 Diagnostic Pathology Full Text. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa;
Endoscopic Mucosal Ablation And Resection Of Barrett S Esophagus And Related Diseases Munoz Largacha Journal Of Visualized Surgery : Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ.
My Gastro Room Barrett S Oesophagus. The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ.
Pathology Outlines Barrett Esophagus , Barrett's Esophagus Is A Complication Of Chronic Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Gerd).
Barrett S Oesophagus For The Histopathologist. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology:
Siu Som Histology Gi . In Barrett Esophagus, Healthy Esophageal Epithelium Is Replaced With Metaplastic Columnar Cells—The Result, It Is Believed, Of Damage From Prolonged Exposure Of The Esophagus To The Refluxate Of.
Barrett S Esophagus And Esophageal Cancer An Overview. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa;
Ppt Figure 5 Histological Features Of Low Grade Dysplasia In Barrett Esophagus Powerpoint Presentation Id 4671361 : Barrett's Esophagus Is A Condition In Which There Is An Abnormal (Metaplastic) Change In The Mucosal Cells Lining The Lower Portion Of The Esophagus, From Normal Stratified Squamous Epithelium To Simple Columnar Epithelium With Interspersed Goblet Cells That Are Normally Present Only In The Small Intestine.
Pathology Outlines Barrett Esophagus. Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus.
Barrett S Oesophagus For The Histopathologist - Barrett's Oesophagus Is A Premalignant Condition That Predisposes To The Development Of Oesophageal Adenocarcinoma.
Pathogenesis And Cells Of Origin Of Barrett S Esophagus Gastroenterology. Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine.
Intestinal Metaplasia Esophagus Histology , Haoxiang Zhang, Caifei Shen, Pu Wang, Ji Feng, Yin Xu.
Barrett Esophagus Histology And Pathology For The Clinician. In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer.
Figure 8 From Histology Of Metaplasia And Dysplasia In Barrett S Esophagus Semantic Scholar , Barrett's Oesophagus Is A Premalignant Condition That Predisposes To The Development Of Oesophageal Adenocarcinoma.
Prospective Evaluation Of Multilayered Epithelium In Barrett S Esophagus Sciencedirect. We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ.
Increasing Diagnostic Accuracy To Grade Dysplasia In Barrett S Esophagus Using An Immunohistochemical Panel For Cdx2 P120ctn C Myc And Jagged1 Diagnostic Pathology Full Text : Find Out All The Facts And Barrett's Esophagus Symptoms In This Guide.
Histologic Anatomy Abdominal Key. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. The following on histology and immunohistology of barrett's esophagus (be) includes commentaries on the various difficulties remaining in reaching a consensus on the definition of be; The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. In this third (# 3) video of esophageal histology, we will discuss about a very important pathology: Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. Replacement of columnar mucosa to squamous (neosquamous) mucosa; Barrett's esophagus (barrett's disease) is caused by chronic acid reflux that increases the risk of esophageal cancer. We will talk about the diagnostic criteria, the endoscopic examination. The esophagus is typically characterized as having a stratified squamous epithelium that protects against mechanical damage that can be induced by the peristaltic action of the esophagus on food. Find out all the facts and barrett's esophagus symptoms in this guide. These similarities with incomplete intestinal metaplasia are present on histology. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Residual metaplastic epithelium may persist. Barrett's oesophagus is a premalignant condition that predisposes to the development of oesophageal adenocarcinoma.